Everything You Need to Know About Collagen
Article posted in: Diet & Nutrition
Chances are, you’ve heard of injecting collagen into the skin to replenish what has naturally depleted and help smooth facial lines. But have you heard about ingesting it?
Ingesting collagen has become the latest health trend and has many people questioning whether they should add a form of it to their diet. We know there are a lot of questions and you may not be sure what’s best for you. That’s why we’ve done some research and rounded up the facts to tell you everything you need to know about collagen.
Read on to learn about collagen and how it relates to your healthy lifestyle:
What is Collagen?

Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, says Healthline. It’s used to build muscles, cartilage, bones, skins, tendons and more. Healthline describes it as the “glue” that keeps things together.
While our bodies produce it naturally, production decreases with age. Cleveland Clinic explains that this decrease can cause wrinkles, thinning of the gastrointestinal lining, stiff tendons and ligaments, weakening of muscles and joint pain. This is why many have turned to supplementing collagen into their diet.
Benefits of Collagen

While there is not much research on the supplementation of collagen at this time, current studies show potential benefits for skin, muscles and joints, says Healthline. In a study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, women who took a collagen supplement for eight weeks experienced less dryness and an increase in skin elasticity. Another study, published in the Journal of Medical Nutrition & Nutraceuticals, found that post-menopausal women who drank a nutritional supplement beverage containing collagen experienced a decrease in wrinkle depth, increased skin hydration and elasticity.
While more youthful skin is likely the biggest motivation to ingest collagen, there are also other potential benefits such as increased joint, bone and muscle health. A study published in the peer-reviewed journal, Current Medical Research and Opinion, found that healthy athletes at Penn State University who consumed a liquid collagen supplement for 24 weeks experienced less joint pain. Another study, published in the British Journal of Nutrition, found that elderly men with sarcopenia that consumed a protein supplement with collagen after exercise experienced higher levels of bone mass, fat-free mass, isokinetic quadriceps strength and sensory motor control.
Healthline explains that collagen is an essential protein within the human body. Studies show potentially promising benefits of supplementation for skin, joints and muscles. However, more research is needed to evaluate long-term benefits and potential effects.
Collagen Supplements
If you want more youthful skin and less joint pain, speak to your doctor to see if a collagen supplement will be beneficial for you. There are a few types of supplements on the market, with bone broth being one of the more popular options. Cleveland Clinic explains that bone broth is made by simmering beef, chicken or fish bones in water. This releases collagen from the bones, creating a broth. You can buy bone broth in the store or easily make your own at home.
Oral supplements and powders also seem to be quickly gaining popularity. According to Healthline, the powder form can be easily added into foods like shakes, smoothies, stews and baked goods. Topical skin creams also exist. However, Cleveland Clinic explains that these topical creams may not be as effective as a healthy diet and shielding your skin from the elements.
Foods to Boost Collagen

If you don’t wish to add a collagen supplement to your diet, you can consume specific foods with nutrients to help boost your natural production. According to Cleveland Clinic, the body needs amino acids from proteins, vitamin C, zinc and copper to produce collagen.
According to MedlinePlus, sources of these nutrients include:
- Protein: Meat, eggs, fish, beans, soy, nuts and quinoa.
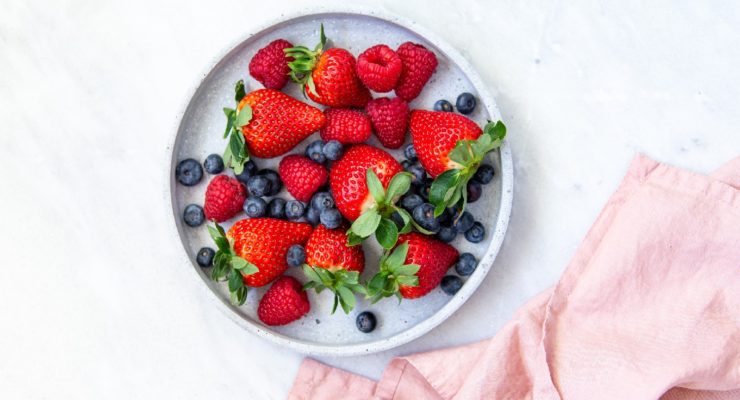
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, tomatoes, strawberries, bell peppers, kiwifruit and broccoli.
- Zinc: Meat, poultry, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds.
- Copper: Shellfish, whole grains, nuts, dark leafy greens, beans and cocoa.
While your boosting your collagen production, make sure that you are also protecting your current stores. Healthline says that sugar and refined carbohydrates cause inflammation and harm to collagen. Eating a healthy diet that is filled with high quality proteins and vegetables, while low in sugar and refined carbs is essential to producing and preserving collagen.
Nutrisystem focuses on a healthy lifestyle that is high in protein and fiber. Get started with a weight loss plan today!
Please Note: Always speak to your doctor before making any changes to your diet.










